공간정보산업
공간정보산업은 공간정보를 생산·관리·유통하거나 다른 산업과 융·복합하여 시스템을 구축하거나 서비스 등을 제공하는 산업으로, 증강현실(AR)과 가상현실(VR)기술의 발달에 따라 공간정보산업은 지속적으로 확대되고 있음 (무인자동차, 무인항공기, 드론 등)
공간정보산업은 공간정보를 생산·관리·유통하거나 다른 산업과 융·복합하여 시스템을 구축하거나 서비스 등을 제공하는 산업으로, 증강현실(AR)과 가상현실(VR)기술의 발달에 따라 공간정보산업은 지속적으로 확대되고 있음 (무인자동차, 무인항공기, 드론 등)
| Required Workers | Required Time | Work Area | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement using drones | 1 | 6 Hours | 881,536m2 | About 30 times of efficie |
| Measurement with Labor | 1 | 6 Hours | 30,000m2 |
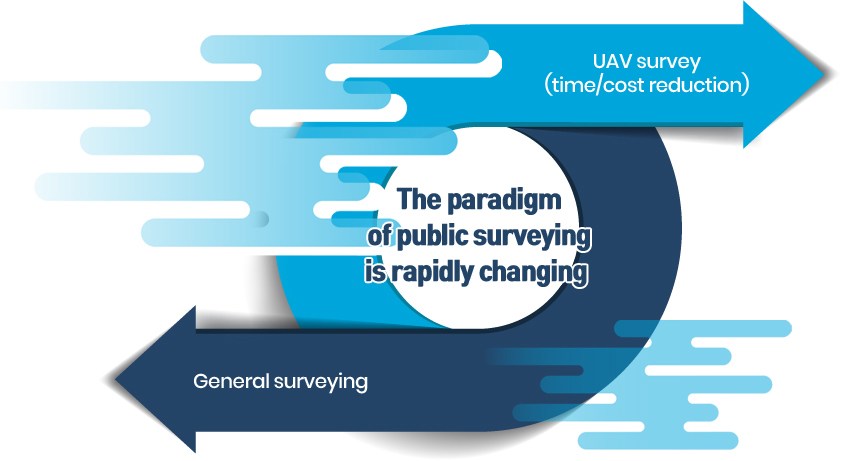
국토교통부 2018년 3월까지 제도 정비, 2018년부터 드론을 활용한 측량 본격화
지상측량 / 유인항공기 촬영을 통해 공공측량을 실시하던 대다수의 업체가 앞으로 드론을 활용하겠다는 의지를 밝힘
2014년 12월 기준 국내 공간정보산업 매출액은 7조 1,273.5억원으로 사업체 전체 매출액 12조 1,145억원의 58.8%를 차지함
국토정보지리원은 연간 약 1천 650억원 규모에 달하는 국내 공공측량 시장 중 항공/지상측량을 드론으로 대체 가능한 시장은 약 300억 원 규모로 예상.(약 18%)
국외 공간정보산업은 측량가 GIS를 기준으로 44억 달러, 포괄적 범위로는 4천억 달러까지 추정됨 (세계 공간정보산업분야, 국가공간정보포털)
공간정보산업분야는 지속적으로 성장
| Surveying + GIS | Surveying + GIS + Applied Technology | Surveying + GIS + Applied Technology + Fused & Converged Industries |
|---|---|---|
| 4.4 billion USD | 60 ~ 80 billion USD | 400 billion USD |
| Daratech (2008) | IDC(2008), Gartner(2008) | METI (Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (Japan), 2008) |
| GIS-related H/W, S/W / Data Service | LES, ITS, GIS-related applied technology & service industries included | Including Ubiquitous Intelligence Services |
세계 공간정보산업 분야, 국가공간정보포털(http://www.nsdi.go.kr)
| Country | US | Canada | France | Germany | England | China | Japan | Korea | Australia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit (100 Million $) | 350 | 200 | 85 | 60 | 25 | 13 | |||
| Share (%) | 45 ~ 50 | 25 ~ 30 | 9 ~ 12 | 6 ~ 11 | 3 ~ 4 | 1.5 ~ 2 | |||
공간정보산업 해외 원조사업 활용 활성화 전략 연구
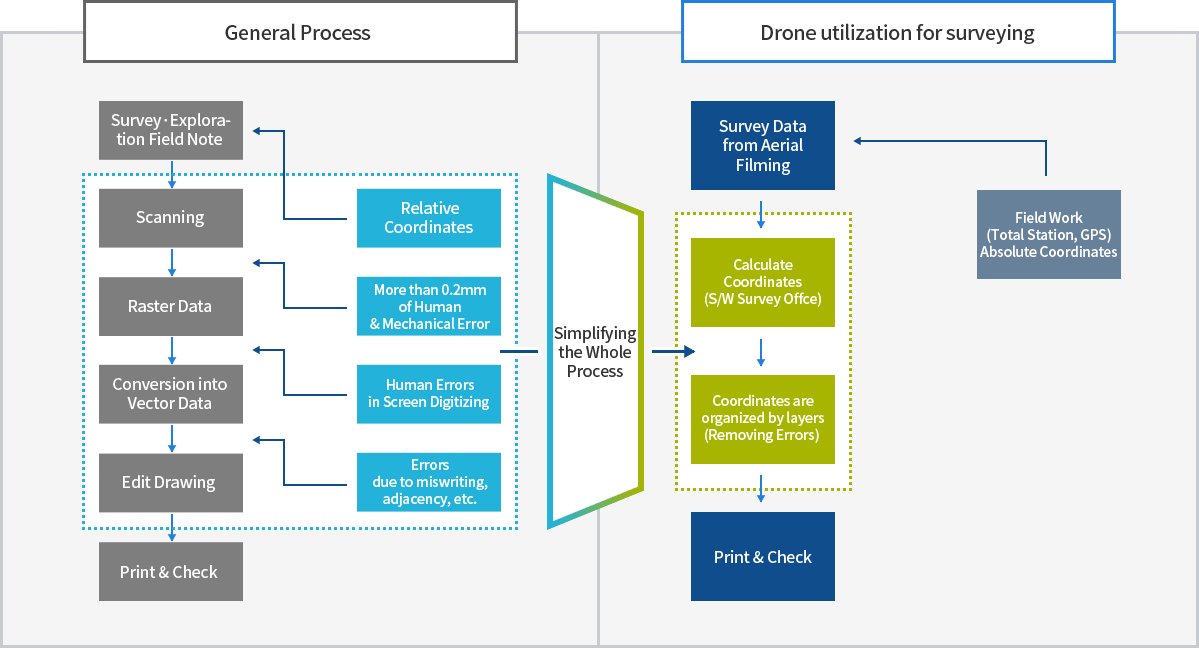
각 공정별 누적오차가 산재되어 정확도 확보가 어려움
개인오차 발생가능성이 높음
공정단축
작업자에 의한 입력 오차 소거
실시간 측량으로 DB의 정확도 확보
절대측량으로 성과심사 확보방안 모색



VTOL(Vertical TakeOff and Landing) 적용, 수직으로 이/착륙하여 별도의 활주로나 접근공간을 필요로 하지 않음
충돌회피 시스템
직선입 타입
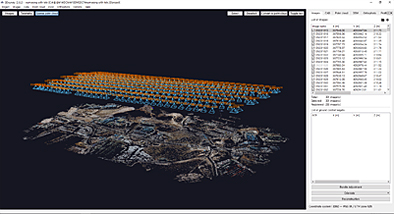
초벌 작업

3D 모델링

체적 산출
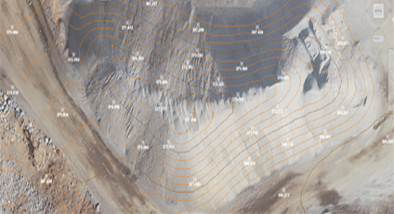
정사영상 확인

각 등고선별 고도 확인
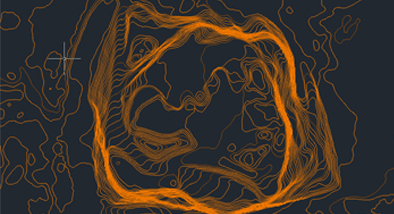
등고선 작업
(주)자이언트드론은 드론을 활용한 측량으로 여러가지 측량 업무를 수행하고 있습니다.
국토교통부에서 2017년 하반기에 야간 및 비가시권 특별비행을 위한 안전기준과 승인절차에 관한 기준을 고시함.(항공안전법 제 129조 5항)
무인비행장치 특별비행을 위한 안전기준 및 승인절차에 관한 기준
특별비행 안전기준 (제4조 관련)
| Classify | Main Components | |
|---|---|---|
| Commons Requirements | Obstacles in landing and flight paths must not affect flight safety | |
| Must equip Fail-safe device | ||
| Must equip collision avoidance feature | ||
| Must equip a separate GPS location transmitter to transmit location information when a crash occurs | ||
| Must prepare and maintain an emergency manual which includes emergency contact & reporting systems in cases of emergency, Also, all participants must undergo emergency training in order to respond properly in the case of an emergency situation | ||
| Detailed Requirements | Night Flying | At least one observer should be placed to keep track the UAV during night flights |
| Must install an anti-collision lamp that can be recognized from 5km away | ||
| Anti-collision lighting must use ‘permanent light type’ and installed in locations where they could recognize in all directions. | ||
| Must equip auto-flight mode | ||
| Must equip FPV which uses an infrared ray camera | ||
| Must install a ground lighting facility and a searchlight at the landing pad. | ||
| Invisible Flights | At least one observer must be located in the planned flight path to identify the UAV when the UAV is flying beyond the visibility of the pilot | |
| Communication must be possible between the pilot and the observer to ensure a steady operation of the UAV | ||
| The pilot must check the pre-planned flight path, and the UAV must be capable of manual/automatic/semi-automatic flight | ||
| The pilot must ensure before the flight that the CCC (Command, Control, and Communication) equipment is usable within the planned flight range | ||
| The UAV must be programmed with the flight plan and the profiles of emergency situations | ||
| The UAV must be able to notify the pilot in case of a system malfunction | ||
| Communication (RF communication, LTE communication backbone network usage, etc.) must be dual-path | ||
| Display the state of the UAV on GCS. GCS notification and external pilot notification in case of abnormalities and failures | ||
| Equipped FPV (First-Person View) | ||